A vitamin D deficiency can have serious consequences for your health. How you can recognize it and why it is worth doing a blood test.
Every cell in your body has a receptor for vitamin D. That’s why it’s more of a hormone than a vitamin and very important for your holistic well-being. If you have a deficiency of the sun vitamin, this is accompanied by a number of symptoms.
Vitamin D deficiency symptoms
The following symptoms can occur in the event of a deficiency:
- Fatigue
- Listlessness
- Mood low
- Decreased libido
- Menstrual cycle disorder
- Dry skin
- Hair loss
- Back pain
- Sleep problems
- Weakened immune system, Common diseases
- Slowed wound healing
You see, they are quite common complaints. They can potentially have various causes. However, you can only find out whether you actually have a vitamin D deficiency by taking a blood test.
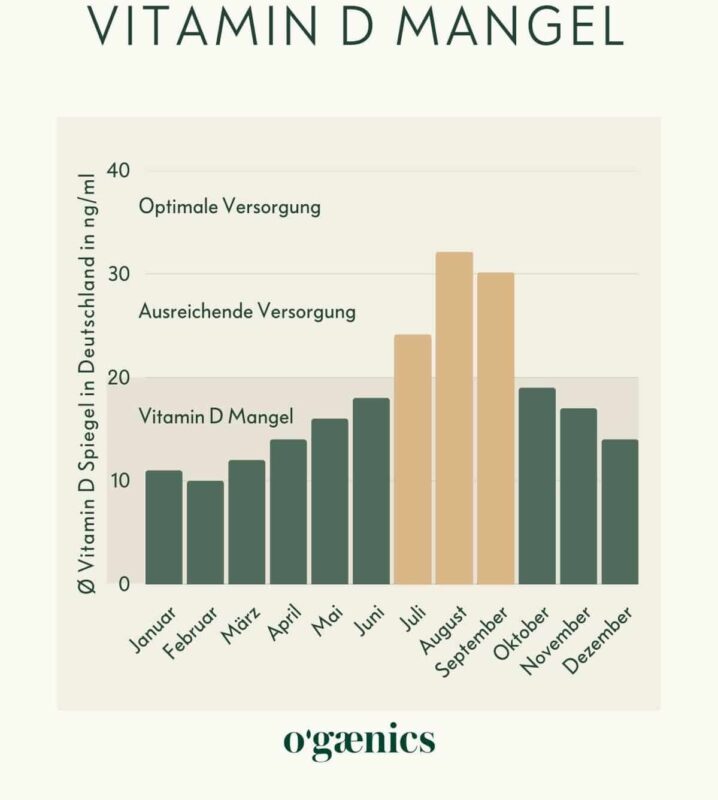
Blood values: when is it a vitamin D deficiency?
According to the Robert Koch Institute, a good vitamin D supply starts at 30 ng/ml. On average, we only just reach these values in Germany, even in the summer months. So we are a vitamin D deficient country. Therefore, the probability that you are also affected is high.
An optimal vitamin D level should be between 30 – 60 ng/ml.
- if less than 20 ng/ml, there is a vitamin D deficiency
- at 20 to 30 ng/ml there is no optimal supply
- 30 to 60 ng/ml are considered optimal values
- 60 to 90 ng/ml are already classified as high values
- at 90 to 150 ng/ml there is an oversupply
- at levels above 150 ng/ml there is a risk of vitamin D poisoning
Vitamin D deficiency: Are you at increased risk?
There are several factors that can increase your risk for vitamin D deficiency. Consider if you are in any of the following situations. You are at increased risk of one if you
- You are older than 65 years. As you age, your skin is less able to make vitamin D from sunlight.
- Exposing your skin to sunlight infrequently because you stay indoors, cover up outdoors, use sunscreen or live in a place where there is little sunlight
- have dark skin, which makes less vitamin D from sunlight
- Suffer from a disease that makes it difficult to absorb nutrients from food, such as Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis and celiac disease.
- Have kidney or liver disease that affects your ability to convert vitamin D into a form your body can use
- you are taking certain medications that affect your vitamin D levels, such as glucocorticoids (= cortisone) and anti-epileptic drugs.
Vitamin D deficiency? Do the test
Ultimately, it’s always important to get your blood work. You can have this done at the doctor’s office or at a lab. You can also measure your vitamin D supply quickly and conveniently with a test kit. A Vitamin D rapid test gives you accurate results within minutes. The quick test is used to determine your vitamin D concentration in the blood.
At Ogaenics, we have an innovative rapid test that guides you through the entire testing process with a vitamin D app on your smartphone. This requires only a minimal amount of blood from the fingertip, which is applied to the test cassette and then evaluated by your smartphone. The concentration of vitamin D (25-OH-D) in the blood is measured, which makes the test strip react in color so that the smartphone can evaluate and display the result. It could not be simpler!
The right dose for vitamin D deficiency
If you have been diagnosed with a vitamin D deficiency, it is important to plan your therapy in collaboration with a specialist. In some cases, it may be appropriate to start with a higher initial dose of up to 4,000 units of vitamin D per day for a limited period of 2-4 weeks to rapidly compensate for the deficiency. However, this initial therapy should always be done under a doctor’s supervision, as individual factors such as your health condition and medical history must be taken into account.
To ensure that you effectively correct your vitamin D deficiency, it is advisable to carry out regular checks using vitamin D tests at appropriate intervals. This allows precise determination of the correct dosage to meet your individual needs. A vitamin D test will help you monitor the progress of treatment and make sure you are not taking an excessive or insufficient amount of vitamin D.
Regularly monitoring and adjusting your vitamin D supplementation is key to successfully managing a vitamin D deficiency and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.






 No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.